ENCRYPTION KEYS: why you should use them
Encryption keys play a critical role in securing enterprise communications, particularly in cloud-based Software as a Service (SaaS) applications. Here's a summary of their importance and how they enhance security in this context:
1. Confidentiality:
Encryption keys are essential for maintaining the confidentiality of data. When data is encrypted, it is transformed into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered using the correct encryption key. In cloud SaaS applications, sensitive business information, customer data, and intellectual property are regularly transmitted and stored. Encryption ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable and confidential.
2. Data Protection:
Cloud environments are inherently multi-tenant, meaning multiple organizations share the same infrastructure. Encryption keys ensure that data from one organization is isolated and inaccessible to others. This prevents data breaches and unauthorized access, safeguarding a company's proprietary information.
3. Compliance Requirements:
Many industries and jurisdictions have stringent data protection and privacy regulations. The use of encryption keys helps enterprises comply with these requirements by ensuring that data is adequately protected, thereby avoiding potential legal and financial consequences.
4. Secure Data Transmission:
SaaS applications often involve the transmission of data between users and the cloud service. Encryption keys are used to secure data during transit, preventing interception or eavesdropping by malicious actors. This ensures that data remains confidential even while in motion.
5. Secure Data Storage:
In cloud SaaS applications, data is typically stored on remote servers. Encryption keys are used to encrypt data before it is stored, adding an additional layer of protection. Even if someone gains physical or unauthorized access to the servers, the data remains encrypted and unusable without the correct key.
6. User Authentication:
Encryption keys are also used for user authentication in SaaS applications. They help ensure that only authorized users can access the system, preventing unauthorized users from gaining entry and potentially compromising sensitive data.
7. Key Management:
Proper key management is crucial to encryption's effectiveness. Enterprises need to securely generate, store, and rotate encryption keys to prevent vulnerabilities. This includes using hardware security modules (HSMs) and implementing key rotation policies.
8. Resilience against Insider Threats:
Encryption keys are essential for protecting data from insider threats, where authorized personnel with malicious intent try to access sensitive information. Strong encryption and access controls limit the potential damage caused by such individuals.
Encryption Keys: Management
Proper key management is crucial to encryption's effectiveness. You should pay attention and ask questions when moving your data to cloud SaaS applications.
1. SaaS Provider Managed Keys:
In this approach, the SaaS provider handles encryption key management, making it user-friendly and reducing IT responsibilities for your small enterprise. However, it may offer limited control and auditability.
Auditability Considerations:
• Limited Visibility: With SaaS provider-managed keys, you may have limited visibility into key usage. The provider controls access to keys, and detailed audit logs might not be readily accessible to you. This limitation can hinder your ability to audit encryption key usage effectively, both by authorized and non-authorized users.
• Compliance Challenges: Meeting specific compliance requirements that mandate detailed key usage audits might be challenging due to the lack of direct control and visibility over key management processes.
2. Customer-Managed Keys:
In this approach, your small enterprise manages its own encryption keys, which provides greater control and visibility over key management and usage.
Auditability Considerations:
• Enhanced Control: Managing your own encryption keys allows you to maintain detailed audit logs of key usage. You can track who accesses the keys, when they are accessed, and for what purpose. This level of control significantly enhances your ability to audit encryption key usage, both by authorized and non-authorized users.
• Compliance Alignment: Customer-managed keys are better suited to meeting compliance requirements that demand rigorous audit trails and reporting of key activities. This can help your organization demonstrate compliance with data security regulations effectively.
Assessment:
The option of Customer-Managed Keys provides a significantly better ability to audit encryption key usage by both authorized and non-authorized users. With control over key management, you can maintain comprehensive audit logs, which are essential for tracking access, ensuring compliance, and identifying potential security breaches.
In contrast, SaaS Provider Managed Keys often offer limited visibility into key usage, making it less effective for auditing purposes. If the ability to audit encryption key usage is a critical requirement for your enterprise, opting for customer-managed keys is the preferable choice, as it provides the necessary control and transparency to maintain robust audit trails.
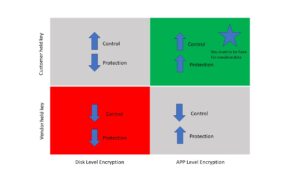
When it comes down to CustomerManagedKeys or BringYourOwnKey, there are actually two different very specific implementation choices, and within those, there's a lot of variation.
The first one we'll talk about is that kind of X-axis disk-level encryption versus app-level encryption.
Disk-level encryption is transparent encryption, and it means that on a running server, the encryption isn't really protecting the data from anybody.
App-level encryption means the data store itself doesn't, you know, it's encrypted before it gets to the data store.
That means if someone gets access to the file system or to the database or to the credentials to access the database or whatever, then what they're getting back is actually encrypted data, which means that if they scrap a database or a search service, they don't really get anything they can use if they didn't somehow also get access to the key.
Disk-level encryption really means it's protecting from stolen hard drives.
Transparent encryption, and that's what actually a lot of people do with this, which is a little bit hand-wavy.
The other thing to talk about is vendor-held keys versus customer-held keys. So, in some of these things, especially when they say BYOK, often that means upload your key to our service, we'll hold it for you, and whenever you want, you can upload a new one, or you could tell us to forget about it, and we promise we'll forget about it. That's managing your keys in a sense. It's managing the keys that are held by the vendor or uploading your own key material. You maybe have a trusted random number generator, and you don't trust theirs or whatever.
REMEMBER: a subpoena can force a provider to decrypt your data if the government asks for it. Access to encryption keys should be under your control, only.
The better level of control is when you hold your own encryption key if you're the customer in your own key management service, and the Saas provider call up to you to be able to do things, but you don't ever have to share that key material with them so they never have the ability to abuse it.